Comment. Commercially available rechargeable batteries are of a maintenance-free type with a sealed case. Such batteries do not have holes for adding water and checking the density of the electrolyte.
To complete the work you will need:
- fine-grained sandpaper;
- voltmeter;
- hydrometer;
- Charger.
Warning! When servicing the battery, you must follow the safety regulations and work with rubber gloves.
Regular battery maintenance
1. We prepare the car for work (see «Preparing the car for maintenance and repair»).
2. We wipe the battery case with a cloth moistened with a 10% solution of baking soda or ammonia, and then with clean water.
3. Check the reliability of the battery on the car (see above, «Battery - removal and installation»).
4. Check the condition of the battery terminals and power wire terminals. If the terminals are covered with a layer of oxides, remove the terminals from the battery terminals. With sandpaper, we clean the battery leads and wire terminals to a shine.
5. We check the electrolyte level in each battery, for this, the MIN and MAX marks are marked on the battery case. If the level is below normal, hydrometer (or medical syringe) add distilled water to the batteries.
Comment. On a battery that has been in operation for several years, the electrolyte level is poorly visible through the case wall. In this case, you can check the level through the filler holes of the batteries. The electrolyte should completely cover the battery separators and slightly not reach the lower edges of the filler wells.
Checking and charging
1. Remove the battery from the car or disconnect the wire terminals from the battery terminals and remove the clamping bar (see above).
2. We turn out the battery plugs (it is convenient to do it with a coin).
3. Using a hydrometer bulb, we select part of the electrolyte into the flask of the device and, without removing the nose of the flask from the filler hole of the battery, we determine the density of the electrolyte in each battery using the floats. Each float is marked with the minimum density at which it floats.

Comment. After topping up with distilled water, until the solution in the accumulator is completely mixed, the hydrometer readings will be incorrect. In a hydrometer with one float, the density is determined by a scale printed on the float, and depends on the depth of its immersion.
The density of the electrolyte in a fully charged battery should be close to that indicated in Table. 13.4.1. in accordance with the climatic zone of operation of the car.
When taking hydrometer readings, it is necessary to take into account the temperature correction. When the electrolyte temperature decreases by one degree, the battery capacity decreases by 1-2%.
Table 13.4.1
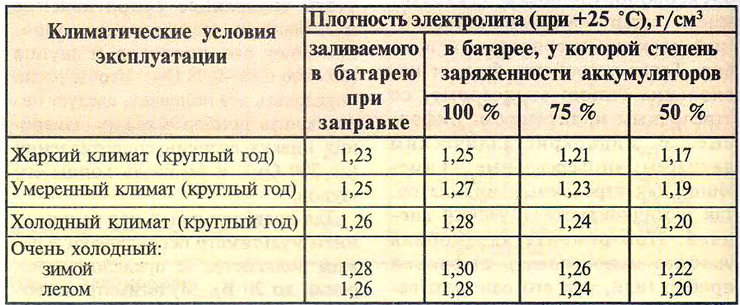
Comment. In the absence of a hydrometer, the degree of charge of the battery can be checked with a voltmeter by measuring the voltage at the battery terminals. By comparing the result obtained with the values indicated in the table, determine the contamination of the battery.
Table 13.4.2
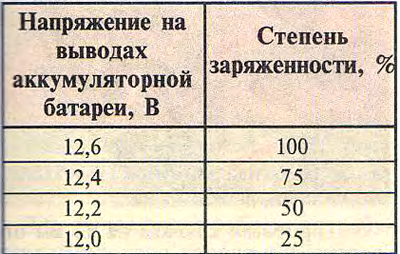
Recommendation. A battery that is 50% or more discharged must be charged.
4. We connect the charger to the terminals of the battery, observing the polarity, and only after that we turn on the charger to the mains. The charging current should not exceed 10% of the battery capacity in amperes, that is, the maximum charge current is 5.5 A.
5. We charge the battery. The process is controlled by measuring the density of the electrolyte. The charging time of a fully discharged battery is at least ten hours at a charging current of 5.5 A.
6. We stop charging the battery after abundant gas evolution begins in all its batteries: first we disconnect the charger from the mains, and only after that we disconnect the wires from the battery terminals.
7. We wrap the plugs in place.
8. We put on the terminals of the power wires on the terminals of the battery. Using a 10 mm spanner wrench, tighten the terminal bolts and apply a thin protective layer of grease to the battery terminals and leads.
