- caliper;
- soft metal rod (∅ 21 mm).
Disassembly
1. Remove the piston rings from the piston (see above).
2. With an awl, we hook and remove the piston pin retaining rings from the grooves.

3. With a soft metal bar of a suitable diameter, we push out the piston pin.

4. Remove the piston from the connecting rod.
Selection of pistons to block cylinders
For new engines, the clearance between the piston and the cylinder is 0.025-0.045 mm and is set by installing pistons of the same class as the cylinder class.
1. With a bore gauge, we check the wear of the cylinder walls (see «Piston and connecting rod - replacement»).
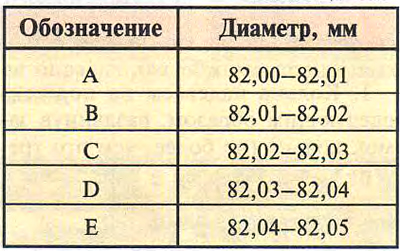
Cylinder diameters divided into five size classes (see table. 16.4). The class of each cylinder is stamped on the lower mating surface of the cylinder block.
Table 16.4. Classes of cylinders by diameter
Recommendation. Small uniform cylinder wear (within 0.05mm) it is possible to compensate by installing a piston of another class with a larger diameter.
If the maximum wear is 0.15 mm or more, it is necessary to bore the cylinders and install oversized pistons.
Cylinder bore of 0.4 mm and 0.8 mm is provided for the dimensions of the repair pistons.
2. On the bottom of the piston are marked, where:
- 2 - hole class for the piston pin;
- C - piston class;
- "left arrow" - arrow for orienting the piston in the cylinder (should point towards the timing drive);
- G - piston mass group.

According to the diameter of the hole for the piston pin, pistons are divided into three classes (1, 2, 3) - through 0.004 mm.
The outer diameter of the pistons are divided into five classes (A, B, C, D, E) - through 0.01mm (measured in a plane perpendicular to the piston pin at a distance of 55 mm from the piston crown).
The size of the pistons are nominal and two repair sizes. Nominal size pistons are not marked. Pistons of the first repair size are manufactured with a diameter increased by 0.4 mm and are marked with a symbol «□». Pistons of the second repair size have a diameter increased by 0.8 mm and are marked with the symbol «□».
On the engine, all pistons must be of the same mass group. Pistons of the nominal group are indicated by the symbol «G». Pistons with an increased and reduced mass of 5 g are indicated «+» And «—» respectively.
The class of the finger is marked with paint on its end.

Comment. The connecting rod and piston group can be equipped with either pins 2108-1004020 with increased wall thickness, or pins 2110-1004020.
Table 16.5. Mass classes of connecting rods
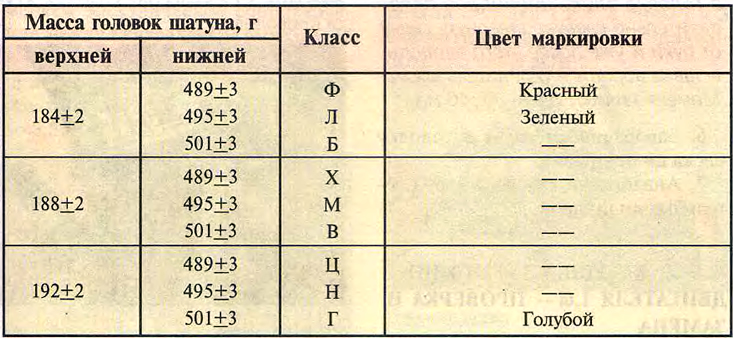
Table 16.6. Piston pin classes by outside diameter and pin hole diameter
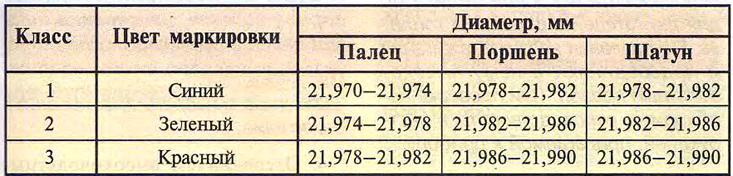
According to the outer diameter, the fingers are divided into three classes (blue, green and red), through 0.004 mm.
To facilitate the selection of a finger to the piston bore, the required class of the finger is indicated on its inner side with paint.

The required pin class is indicated on the connecting rod cap 2. The connecting rods are divided into classes according to the mass of the heads. The marking is applied to the connecting rod cap 1...
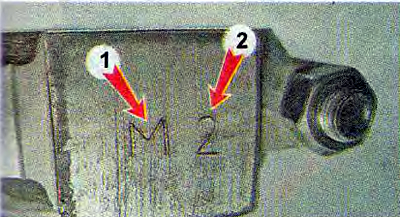
...or paint.
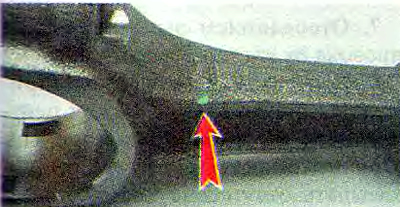
Warning! Connecting rods of the same weight class must be installed on the engine (see table. 16.5).
Assembly
We assemble the piston with the connecting rod in the reverse order of disassembly.
Warning! When assembling the connecting rod with the piston, make sure that the markings on the connecting rod and the markings on the piston face the same direction.
When installing the piston in the cylinder, the connecting rod with the cylinder number should face the side of the block on which the tide for installing the oil filter is located, and the catalog number should face the front end of the crankshaft.
