The air entering the engine cylinders is cleaned of dust by an air filter. The air filter is mounted in the engine compartment on three rubber mounts. The filter element of the filter is replaceable, made of special paper. To prevent the ingress of polluted air into the intake tract, there is a sealing border at the top of the element. To replace the filter element, the filter cover is made removable. The purified air passes through the mass air flow sensor through the air duct to the throttle valve.
The throttle valve controls the amount of air entering the engine cylinders. Pedal damper drive «gas» - cable. The damper rotates on an axis in the housing (branch pipe). The throttle body is studded to the intake module flange. The housing has a channel for the coolant. The channel is connected to the cooling system by rubber hoses. The circulation of coolant through the throttle body prevents freezing of the internal air cavities of the body in winter. Fittings are installed in the housing for connection with the adsorber and the engine crankcase ventilation system.
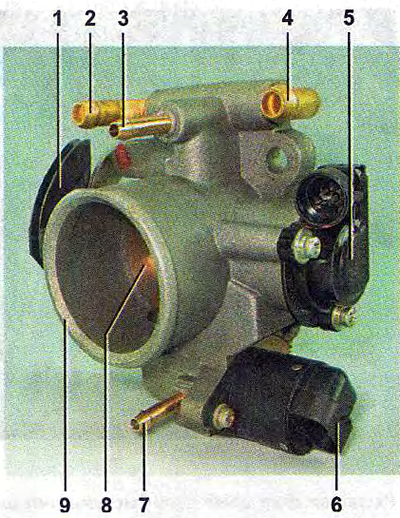
Throttle assembly:
1 - throttle actuator sector;
2, 4 - fittings for connection with the engine cooling system;
3 - fitting for supplying crankcase gases;
5 - throttle position sensor;
6 - idle speed regulator;
7 - fitting for connection with the adsorber;
8 - throttle valve;
9 - branch pipe of the throttle body.
The throttle body with a throttle position sensor and an idle speed controller mounted on it form a throttle assembly.
The stock of fuel is stored in a tank with a capacity of 50 liters. The fuel tank is steel, welded from two stamped parts. The tank is suspended from the bottom of the car on two steel clamps. The filler neck of the fuel tank is displayed on the right side of the car and is closed with a stopper. Fuel from the tank is supplied by an electric submersible fuel pump.
The pump is installed in the fuel tank. To access the pump in the bottom of the car, under the rear seat cushions, a hatch with a cover is made.
A strainer is installed on the fuel pump inlet pipe to trap small solid particles of debris that have entered the fuel tank along with gasoline. The pump is energized by the ECU when the ignition is turned on. If at the same time an attempt is not made to start the engine, then after 2-3 seconds the ECU will turn off the fuel pump *

Fuel pump:
1 - protrusion for attaching a mesh filter;
2 - fuel intake pipe for connecting a strainer;
3 - body;
4 - electrical connector block;
5 - day off (forcing) branch pipe for connection with the cover of the fuel module with a corrugated tube.
From the pump to the corrugated tube of the fuel module (see below) gasoline enters the fuel line and then to the fuel filter, where the fuel undergoes a more thorough cleaning.
Fuel filter - paper, installed in a metal non-separable housing.
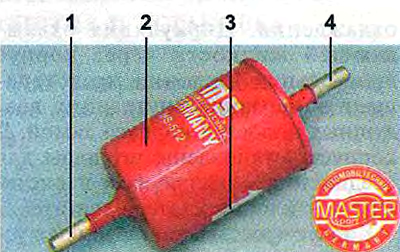
Fuel filter:
1 - inlet pipe;
2 - body;
3 - fuel flow direction arrow (painted on the filter body);
4 - outlet pipe.
The purified fuel enters the fuel rail through the fuel line.
The fuel rail holds the four injectors and delivers fuel to them. The connection of the ramp with the nozzles is sealed with rubber rings. The ramp is bolted to the cylinder head.
The fuel pressure regulator is a bypass valve that maintains in the system (fuel line) working pressure 378-390 kPa, necessary for the correct operation of the injection system.
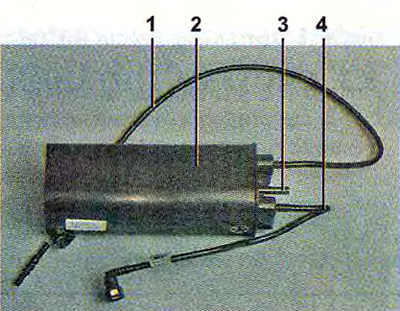
Adsorber:
1 - tube connecting the adsorber with the separator;
2 - adsorber body;
3 - branch pipe for connecting the internal cavity of the adsorber with the atmosphere;
4 - a tube for connecting the adsorber with the adsorber purge valve.
In accordance with current environmental requirements, the car is equipped with a fuel vapor recovery system, the fuel space of the tank is connected to the atmosphere not directly, but through the elements of this system. The system consists of a separator, an adsorber, an adsorber purge valve, connecting pipes and hoses. The separator is fixed under the left rear wing of the car. In the separator, gasoline vapors are partially condensed and returned through the filler pipe back to the fuel tank.
From the separator, uncondensed gasoline vapors through pipes and connecting hoses enter the adsorber, which prevents vapors from entering the atmosphere. An adsorber is a container where gasoline vapors are absorbed by activated carbon. When the engine is running at a high crankshaft speed, the ECU sends a signal to open the canister purge valve, and gasoline vapors are sucked into the intake module receiver.
The adsorber is fixed on the fuel tank on the left and is closed by a protective screen.
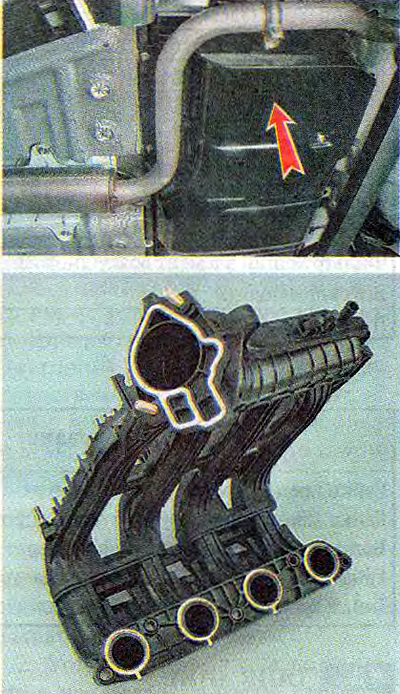
intake module
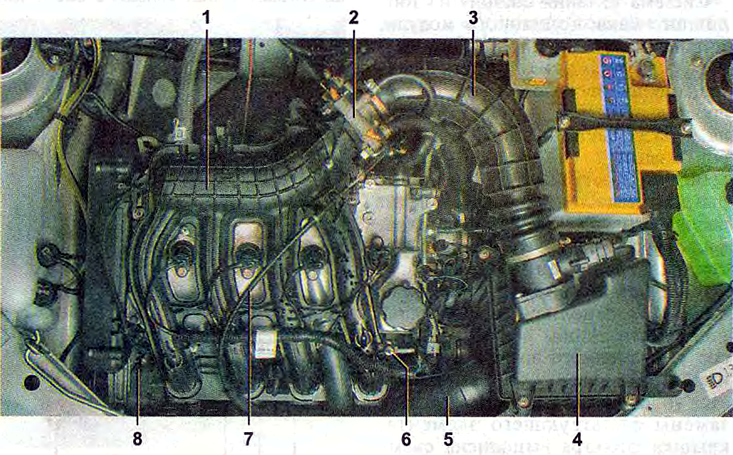
The location of the elements of the engine power system in the engine compartment:
1 - inlet module;
2 - throttle assembly;
3 - air supply hose to the throttle valve;
4 - air filter;
5 - air intake;
6 - fuel rail;
7 - throttle cable;
8 - diagnostic fitting of the fuel rail.
Note. Engine with trim removed.
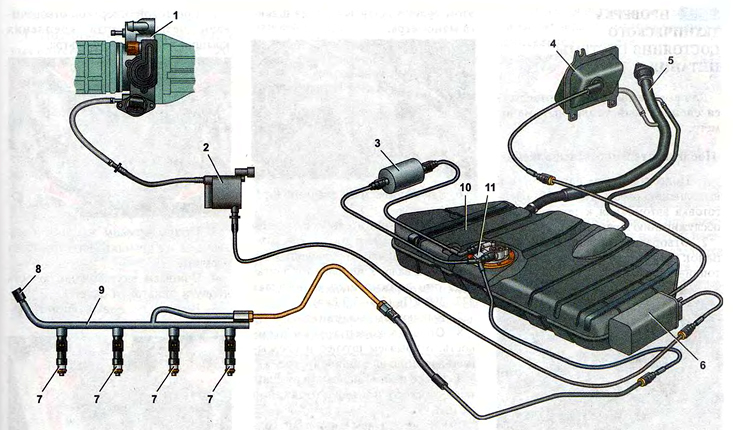
Scheme of the engine power system:
1 - throttle assembly;
2 - adsorber purge valve;
3 - fuel filter;
4 - separator;
5 - filling pipe;
6 - adsorber;
7 - nozzles;
8 - diagnostic fitting of the fuel rail;
9 - fuel rail;
10 - fuel tank;
11 - fuel module.
Air is supplied to the intake valves of the engine cylinders through the intake module.
The engine intake module is made of special plastic and is a non-separable element.
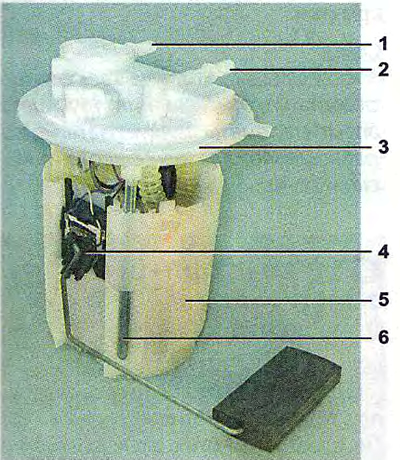

Engine fuel module:
1 - inlet pipe (for supplying fuel to the pressure regulator);
2 - day off (forcing) pipe branch;
3 - module cover;
4 - fuel gauge sensor;
5 - intake chamber;
6 - module cover guide.
The filler cap has two valves: one for emergency release of fuel vapor pressure from the tank (what happens when the ambient temperature rises), and the other - for the intake of air from the atmosphere when fuel is consumed from the tank (this eliminates the occurrence of a strong vacuum in the tank).
The fuel pump is combined with the fuel level indicator sensor and the fuel pressure regulator into a single unit - the fuel module (often referred to as an electric fuel pump).
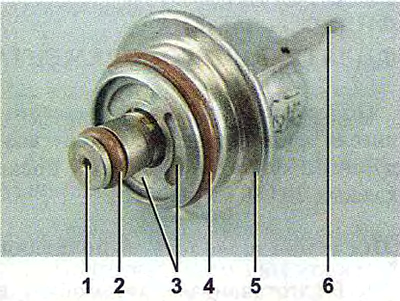
Engine fuel pressure regulator:
1 - hole for dumping excess fuel;
2, 4 - sealing rings;
3 - holes for supplying fuel to the regulator;
5 - body;
6 - output for connecting the regulator with «weight».
Fuel from the pump (through the fuel module outlet) enters the fuel filter. The purified gasoline is again fed through the fuel line and through the tee to the inlet pipe of the fuel module and then fed into the fuel rail. Excess fuel is bled through the pressure regulator into the tank. The fuel pressure regulator is located in the fuel module cover.
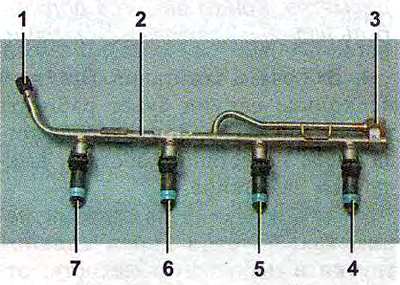
Fuel rail of the engine assembly with injectors:
1 - diagnostic fitting (for checking the operating pressure, closed with a screw cap);
2 - fuel rail;
3 - fitting for connection with the fuel line;
4, 5, 6 and 7 - nozzles.
