1. Normal candle.

Brown or greyish-yellowish color and slight wear of the electrodes. Exact match of the thermal value of the spark plug for the engine and operating conditions.
Note. When replacing spark plugs with new ones, install spark plugs with the same characteristics recommended by the manufacturer.
2. Soot deposits.

The deposition of dry soot indicates a rich air-fuel mixture or late ignition. Causes misfiring, difficult starting and erratic engine operation. Check if the air filter is clogged, if the coolant temperature and intake air temperature sensors are working.
Note. use more «hot» candle.
3. Oil deposits.

Oily electrodes and spark plug insulator. The reason is oil getting into the combustion chamber. Oil enters the combustion chamber through valve guides or piston rings. Causes difficult starting, cylinder misfiring and «twitches» running engine. It is necessary to repair the cylinder head and the piston group of the engine. Replace spark plugs.
4. Metal-containing plaque.

Deposits on the skirt of brick-red iron oxides from anti-knock iron additives (ferrocenes) to gasoline. Lay down in an even, dense layer. When the engine is running under heavy load, under the influence of high temperature and pressure in the combustion chamber, the oxides are reduced into conductive paths of pure iron, which close the central electrode to «mass». This causes misfiring and, as a result, a drop in engine power and increased fuel consumption. In addition, the exhaust gas catalytic converter can be damaged, which overheats greatly when gasoline that has not burned out in the engine cylinders enters it. Plaque is practically not removed mechanically and does not burn out during prolonged movement at high speed. If this plaque appears on new spark plugs after a short run, change the place of refueling.
Note. If it is not possible to immediately replace the candles with new ones, try to remove this coating by immersing the candles with skirts of insulators in phosphoric acid or a rust converter for ten minutes (contains phosphoric acid). After that, clean the plaque with a non-metal brush (maybe with an old toothbrush) and rinse the spark plugs first with water and then with gasoline.
5. Melted electrodes.

early ignition. The insulator is white, but may be dirty due to spark gaps and deposits from the combustion chamber falling on it. May cause engine damage. It is necessary to check the type of spark plug, the cleanliness of the injector nozzles and the fuel filter, the operation of the cooling and lubrication systems.
6. Ash deposits.
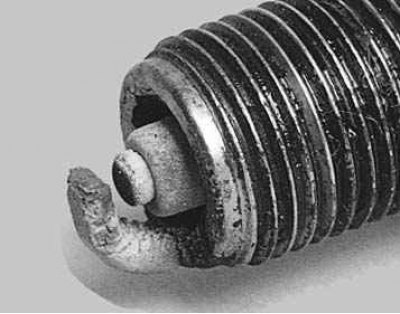
Light brown deposits crusting the center and side electrodes. They are isolated from additives to oil or gasoline. Too many can insulate the spark plug electrodes, causing misfiring and misfiring during acceleration. If excessive deposits form in a short time or at low mileage, replace the valve guide valve stem seals to prevent oil from entering the combustion chamber.
Note. If deposits form consistently over long runs, the reason is the quality of gasoline - change the place of refueling.
7. Candle insulator cracked or chipped.

The reason is detonation, which can damage the piston. Make sure the octane rating of the gasoline is correct.
8. Mechanical damage to the electrodes and the spark plug insulator.
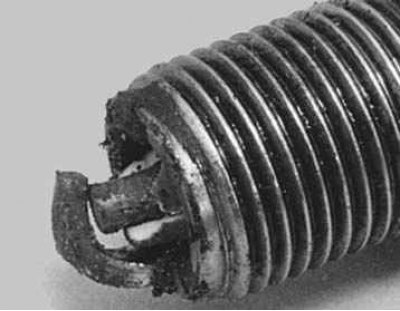
Damage can be caused by foreign objects entering the combustion chamber, and if too long a spark plug is used, its electrodes can catch on the piston. This leads to the destruction of the candle, the shutdown of the cylinder and may damage the piston. Remove the foreign object from the cylinder and (or) replace the spark plug.
