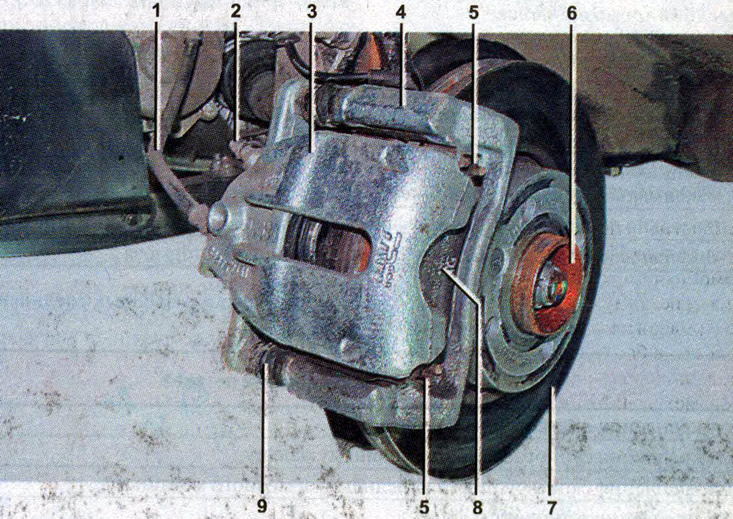
Front brake mechanism: 1 - brake hose; 2 - bleed valve; 3 - support; 4 - brake shoe guide; 5 - spring stops of brake pads; 6 - hub; 7 - brake disc; 8 - brake shoe; 9 - protective cover of the guide pin
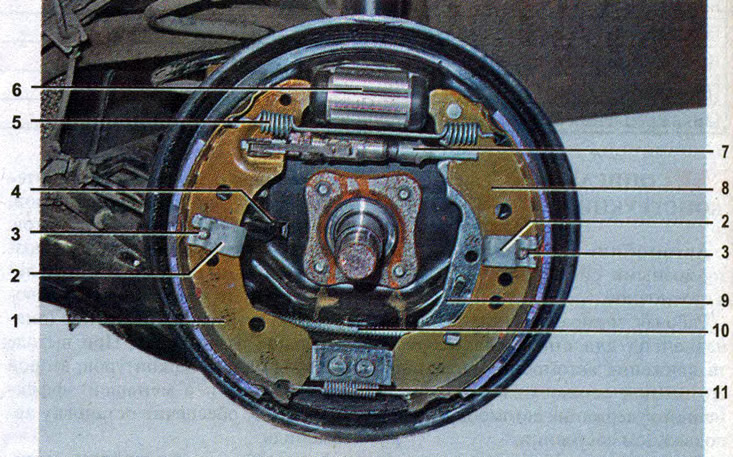
Rear brake assembly: 1 - brake shoe (anterior); 2 - spring bracket for fastening the support post; 3 - support stand for fastening the brake shoe; 4 - wheel speed sensor; 5 - coupling spring (upper); 6 - brake cylinder; 7 - adjusting mechanism; 8 - brake shoe (rear); 9 - parking brake drive lever; 10 - parking brake cable; 11 - coupling spring (lower)
The car is equipped with two brake systems - working and parking.
The service brake system is designed to reduce the speed of the vehicle up to its complete stop and briefly hold the vehicle in a stationary state.
The parking brake system is designed to prevent spontaneous movement of the vehicle during parking.
The working brake system is dual-circuit with a hydraulic drive, consists of a master brake cylinder with a vacuum booster, four brake mechanisms, brake pipelines and hoses. One circuit includes the brake mechanisms of the right rear and left front wheels, the second - the left rear and right front (diagonal division). If one of the circuits fails, the second circuit, albeit with less efficiency, will ensure the car stops.
The car is equipped with an anti-lock brake system (ABS), which prevents the wheels from locking during heavy braking and braking on slippery surfaces. The ABS system uses four wheel speed sensors.

Front wheel speed sensor | 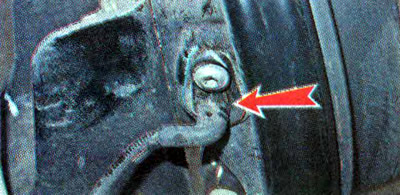
Rear wheel speed sensor |
The driving rings of the front wheel rotation speed sensors are made integral with the outer hinges of the wheel drives, the rear wheels are mounted on the brake drums.
The ABS actuator is a valve body that is installed in the hydraulic drive of the working brake system between the main and working brake cylinders.
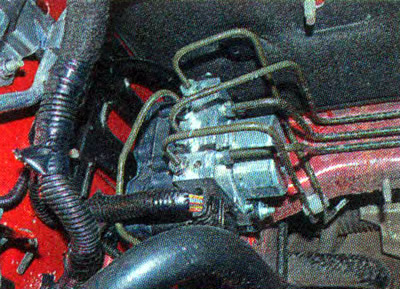
ABS valve body
Comment. The valve body is a complex assembly in which an electrically driven hydraulic pump and solenoid valves are integrated. The operation of the hydraulic unit is controlled by an electronic control unit, combined with it into an integral unit. The control unit also monitors the health of all elements of the ABS system. The pulse signals of the wheel speed sensors are sent to the control unit. When the wheels start to lock, the hydraulic unit, at the command of the control unit, limits the pressure in the hydraulic drive, reducing the braking force.
The brake mechanisms of the front wheels are disc, the mechanisms of the rear wheels are drum.
To reduce the effort applied by the driver to the brake pedal, a vacuum booster is installed in the brake system drive, which operates due to the vacuum formed in the inlet pipeline of a running engine.
Warning! Do not turn off the engine until the vehicle has come to a complete stop, as this will greatly increase the force that must be applied to the brake pedal to stop the vehicle.
A reservoir with brake fluid is installed on the body of the master brake cylinder. The brake fluid level sensor is located in the reservoir. In the event of a dangerous drop in the fluid level in the tank, the sensor sends a signal to turn on the warning lamp for insufficient brake fluid level on the instrument panel.
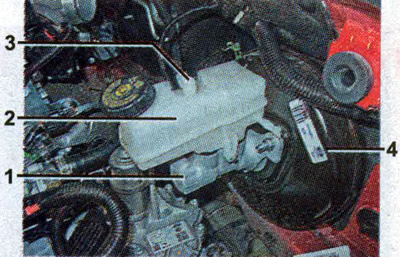
Master brake cylinder: I - the main brake cylinder; 2 - tank; 3 - emergency brake fluid level sensor; 4 - vacuum brake booster
The parking brake system is driven by cables to the brake mechanisms of the rear wheels. When used correctly, the parking brake system requires no maintenance. However, sometimes it may be necessary to adjust the drive (cm «Parking brake - adjustment»).
We check the technical condition of the brake system in accordance with the maintenance regulations (see «Maintenance plan»).
